Extractions
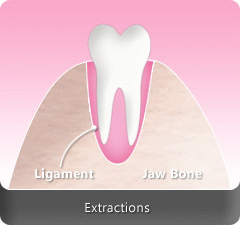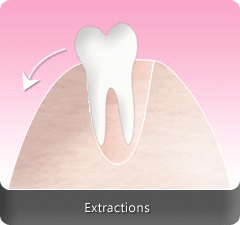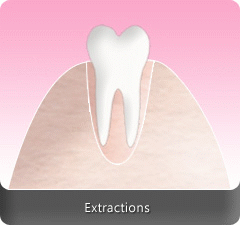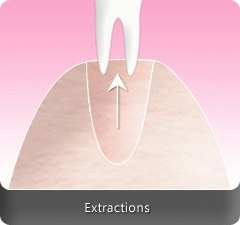
Tooth extraction or dental extraction is the removal of tooth from the mouth. This can also be the basis for future cosmetic dental treatments.
Extractions can be simple or surgically done. Simple extractions are usually performed when the tooth is visible, already loose and only require dental forceps to lift it after it has been rocked back and forth. On the other hand, surgical extraction involves the removal of teeth that cannot be easily accessed because they have not fully erupted or they have broken under the gums. This requires an incision and frequently, the tooth to be extracted are split into multiple pieces to be able to easily remove it.
The following conditions may require tooth extraction procedure:
- Teeth that are rotten which cannot be repaired to prevent infection
- For orthodontic treatment, a tooth needs to be removed to create space
- Damaged teeth brought about by injuries such as trip or falls and sports accidents
- Gum disease that affects the tissues and sockets in the gum that hold the teeth in place making it to become loose
- Overcrowded teeth which is the result of having a smaller jaw
- Eruption of wisdom teeth which can affect the positioning and spacing of other teeth
When your dentist decides that a tooth has to be extracted, he may either do it on your regular checkup or schedule an appointment for this procedure. Cosmetic dental options may be recommended afterwards.
Wisdom teeth, also called third molars, usually make their first appearance in young adults between the ages of 15 to 25. Because most mouths are too small for these four additional molars, an extraction procedure, sometimes immediately after they surface, is often necessary.
The following symptoms may indicate that the wisdom teeth have erupted and surfaced, and should be removed before they become impacted, meaning, the teeth have surfaced and have no room in the mouth to grow. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently.
Symptoms may include:
- pain
- infection in the mouth
- facial swelling
- swelling of the gumline in the back of the mouth
Your dentist may recommend an immediate removal of the wisdom teeth, as early removal will help to eliminate problems, such as an impacted tooth that destroys the second molar.
Problems associated with impacted wisdom teeth:
- bacteria and plaque build-up
- cysts development (a fluid-filled sac)
- tumor development
- infection
- jaw and gum disease
Extraction on the wisdom teeth may be done in your regular dentist’s office or you may referred out to an oral surgeon.